Last update: 29 September 2015
Introduction
Precautions must be taken when prescribing medicines for special populations, such as children, the elderly, pregnant and breastfeeding women, and patients with renal or hepatic (liver) impairment. Many of these special precautions are considered in the public documentation of the medicine, in particular, the Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) and the package leaflets (PLs).
Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) – Information guiding healthcare professionals and patients
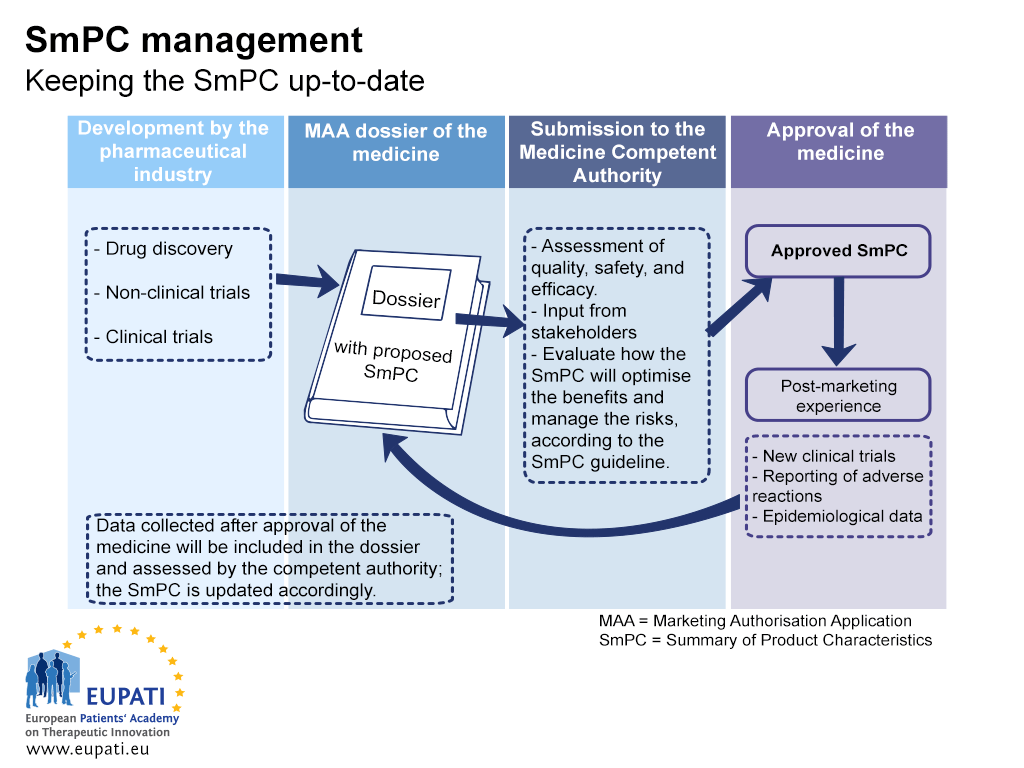
When a company applies for marketing authorisation, the application dossier includes a description for healthcare professionals on how to use the medicine safely and effectively. In Europe, this document is the Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC). The SmPC has to be updated throughout the lifecycle of a medicine as new efficacy or safety data emerge. The figure below shows the relationship between the development of a medicine, the regulatory dossier with the proposed SmPC, the approved SmPC, and the updated SmPC.
- The Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) must be kept up-to-date throughout the lifecycle of a medicine.
The SmPC is also the basis for the preparation of package leaflets (PLs) that come with a medicine, which bring important information on medicines to patients.
The SmPC has a standard format and legally required content. It also contains a section on clinical particulars. This section includes information on the dose and using the medicine:
- in paediatric and elderly populations;
- in patients with organ impairment or other ongoing (concomitant) disease(s);
- in patients with a particular genotype;
- in patients belonging to an ethnic sub-group;
- where interaction with other medicines and other forms of interaction is a factor; and
- in patients who are fertile, pregnant, or breast-feeding women.
Dose
The dose of the medicine is one of the most important pieces of information in relation to special populations and is specified for each indication and each relevant subpopulation.
Children
Children are a specific subpopulation, and it is common for medicine to be used differently in this group or some subsets of it. Therefore, the SmPC is required to contain compulsory information in several sections, addressing the appropriate use of the medicine in children.
Elderly
Information on the use of the medicine in the elderly population may be presented in subsections of the SmPC if clinically relevant differences are known, for instance the need for a dose adjustment, specific risks, and metabolism.
Fertile, pregnant, and breastfeeding women
Information is provided in the SmPC regarding the use of the medicine during pregnancy. Recommendations are also given regarding whether or not to continue breastfeeding while on the medicine.
If contraception is required during and/or after the treatment, this information will be provided along with the rationale behind the recommendation.
Patients with renal (kidney) or liver (hepatic) impairment
Patients with renal or hepatic impairment may require dose adjustments due to potentially altered medicine metabolism or excretion. The SmPC provides information on these possible dose adjustments as well as on the differences in the medicine’s pharmacokinetic profile.
Ethnic sub-groups
When available and clinically relevant, information regarding specific characteristics of the medicine in ethnic sub-groups is presented in the SmPC. These might be indication or dose adjustments, contraindications, or other safety information. For instance, the prevalence of sickle cell anaemia in those of African descent may require special considerations when taking the medicine.
Further Resources
- European Medicines Agency (2023). How to prepare and review a summary of product characteristics. Retrieved 18 February, 2024 from https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview/marketing-authorisation/product-information-requirements/how-prepare-and-review-summary-product-characteristics
A2-5.35-v1.1